The following question types can be used in OpenOlat tests:
Each question gets a short title.
Type of question | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Single Choice | A single-choice question comprises a question and at least two answers; only one of them can be selected. In a test only one of those two answers is correct. First a short title and a question are inserted. Afterward it need to be selected, if the questions should be shuffled, if the alignment of the questions is vertically or horizontally and if the check-boxes are aligned left or right. Then the answer texts can be added. Additional answers can be added with the button . Questions can be deleted with the button . The correct answer can be selected in column Correct Answer. The order of the questions can be changed with the arrows. | |
Multiple Choice | A multiple-choice question comprises one question and at least two answers; several answers can be selected. In a test several answers can be correct. First a short title and a question are inserted. Afterward it need to be selected, if the questions should be shuffled, if the alignment of the questions is vertically or horizontally and if the check-boxes are aligned left or right. Then the answer texts can be added. Additional answers can be added with the button . Questions can be deleted with the button . The correct answer can be selected in column Correct Answer. The order of the questions can be changed with the arrows. In the tab "Score" obviously the score can be defined as well ad the method of assessment. Additionally the "Max. number of possible answers" and the "Min. number of possible answers" can be defined. | |
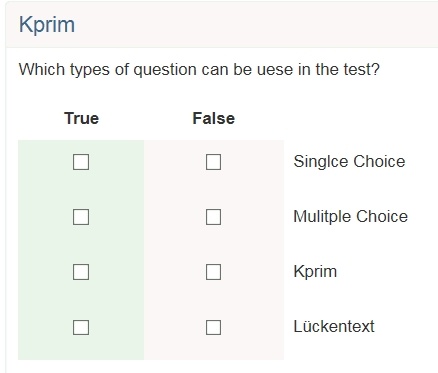
Kprim | A Kprim question can only be used in a test. It comprises one answer and exactly four answers. The one taking that test has to decide for every single answer if it is correct or not. 0 to 4 answers can be correct. First a short title and a question are inserted. Afterward it need to be selected, if the questions should be shuffled and if the check-boxes are aligned left or right. Then answer texts can be inserted. The order of the questions can be changed with the arrows. No more answers can be added and no answers can be deleted. For every answer it must be chosen, if it is true or false. For the assessment, the following score can be reached: All correct answers = 100% score | |
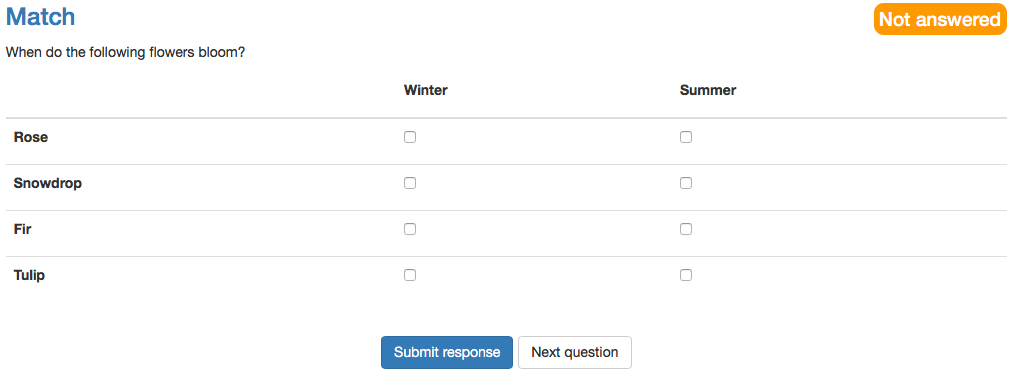
Matrix | A matrix question consists of several rows and columns, where the answer can be filled in for every row, either as single choice or as multiple choice. Again first a title and the question are inserted. Afterward it need to be selected, if the questions should be shuffled and if the answers are single or multiple choice. Then values can be added in the columns as well as in the rows. If more columns or rows are needed, they can be added with the corresponding button. Finally, the correct answer need to be selected per row. For single choice it is one answer per row, for multiple choice several answers per row are possible. | |
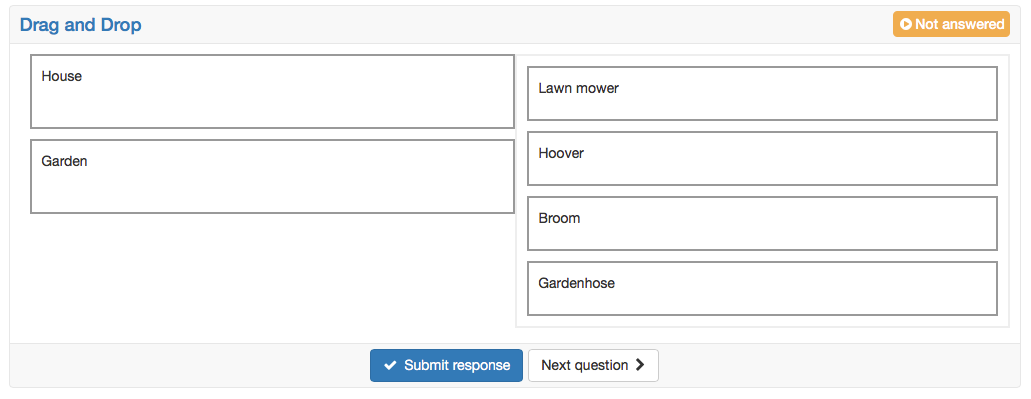
Drag&Drop | In general the Drag&Drop questions has the same behavior as the matrix question. However, the test participants do not select the checkboxes, but move the items in the corresponding category. First a title and the question are inserted. Afterward it need to be selected, if the questions should be shuffled. If the type single choice is selected, every item can be dropped only once. For multiple choice every item can be dropped in every category once, but not twice in the same category. The alignment of the answers defines where the items in relation to the categories are set. In the columns categories will be defined. Categories are the fix elements where the items will be dropped into. In the rows the items are added. With drag&drop the items can be moved into the categories afterward. | |
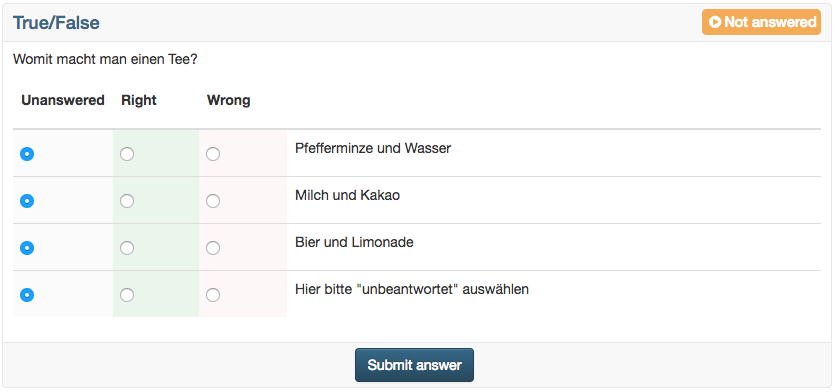
True/false | The question type True/False is similar to Kprim. In each line the corresponding statement has to be assessed. User can choose from three options: "Unanswered", "Right", "Wrong". "Unanswered" is selected by default. There is no option to add more columns. However, you can add as many lines as required by clicking on "Add row". The scores can be defined as needed. You may even give points for the option "Unanswered". | |
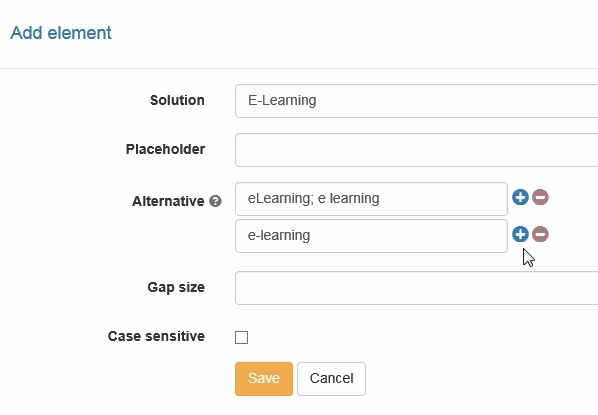
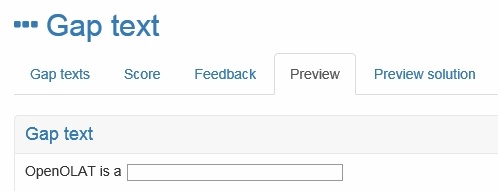
Gap text | In a gap text question the sought terms are replaced by empty fields, which need to be filled in by the participants. Gaps are added with the icon in the editor and with a click on the gap it can be edited. For every gap the following attributes can be filled in:
The points can be chosen freely. Points can also be awarded for alternative answers. The entry of the same answer in several gaps can be allowed or disallowed. |
|
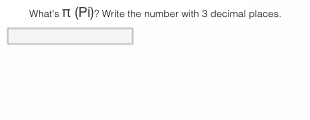
Numerical input | In general the numerical input is the same as the gap text. But as solution there are numbers and no texts required. First a short title is inserted. Afterward the next is written with fields for the gaps. For every gap the following attributes can be filled in:
| |
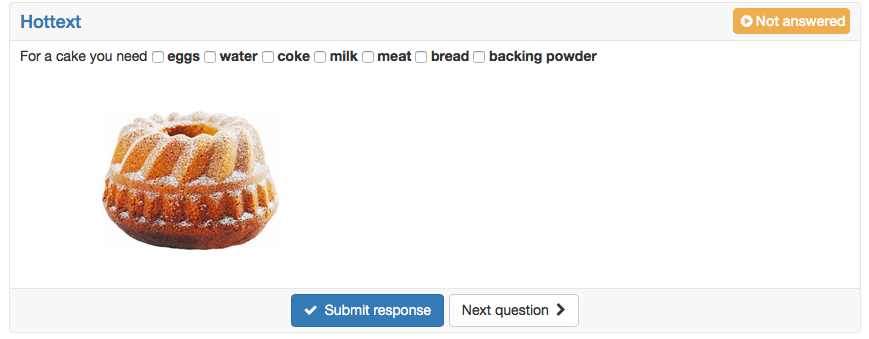
Hottext | The hottext questions is similar to the gap text. In a running text different terms are marked, and can then be selected by the test participants. First a short title is inserted. Afterward a text is written and the selectable terms are marked as hottext. Finally the correct answers need to be marked by selecting the check boxes. | |
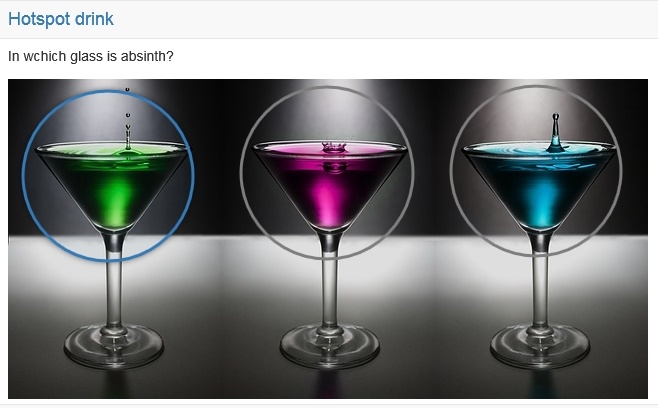
Hotspot | In a hotspot questions hotspots/areas are graphically presented on an image and need to be selected by the participant correctly. Thereby the question can be created either as single or as multiple choice. Various fine adjustments as the hot spot form or color, the adjustment of the size etc. allow an optimal visualization. The spots are visible for the participant. Approach: First a short title and a question are inserted. Afterward the desired picture is uploaded. Than spots in form of circles or rectangles can be placed on the image.Finally, the correct answer need to be selected. | |
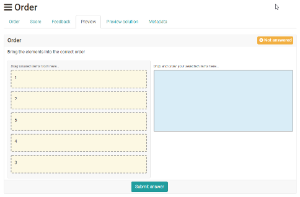
Order | This type of question requires learners to put elements (text or images) in a correct order. This question type behaves similar to a drag and drop question. First the title and the question are entered. Then the answers can be entered in the correct order and the alignment of the display can be set vertically or horizontally. | |
Essay | The answer to a free-text question is inserted into a field of variable size. In a test environment, the free-text question must be evaluated separately and manually. First a short title and a question are inserted. Afterward the following attributes can be chosen:
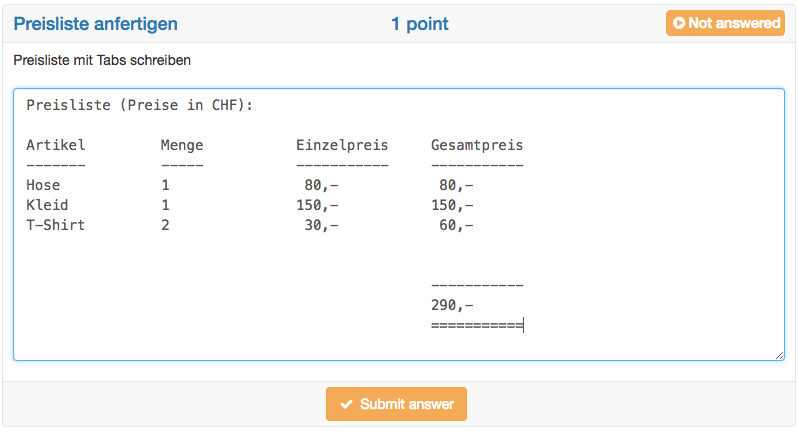
Free-text questions come with a pre-defined width and a tab function. Hence, answers can be formatted more easily, e.g. by displaying columns. Essay questions must be assessed manually and the final score need to be adapted in the assessment tool. Autosave As the name already says it, with this question type essays are written often. Thus this question type has got an autosave feature, which saves written text every minute. Further information about the configuration of essays can be found in the excursion below this table. | |
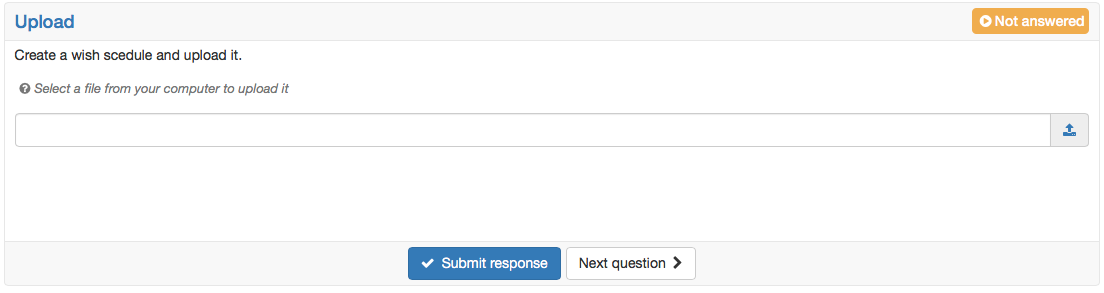
File upload | For this question type participants need to upload a file. A short title and a question is inserted. No correct answer can be marked, as the assessment of this question type is only possible manually. | |
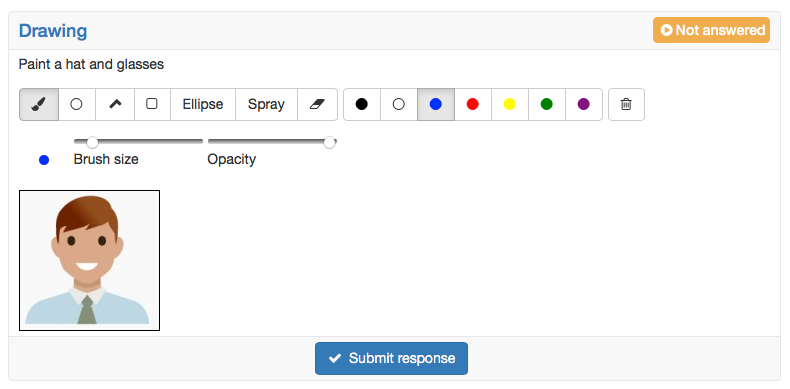
Drawing | For the questions type drawing the participant get the task to edit a given picture with the available drawing tools. First a short title and a question, or more an edit instruction are inserted. Afterward a picture for the background is uploaded. This picture need to be edited by the test participants. No answer need to be added, as the assessment of this question type is made only manually. |
Beside the direct creation, questions can also be imported out of the pool (question bank) or by excel.
Digression